They have properties similar to carboxylic acid
Halogenoacids
Mostly crystalline and toxic
The closer is a halogen atom to the carboxyl group, the acid is stronger
The higher the number of halogen atoms in the molecule, the acid is stronger
Hydroxy acids
Crystalline
They are prepared by hydrolysis of the sodium salts of halogen acids
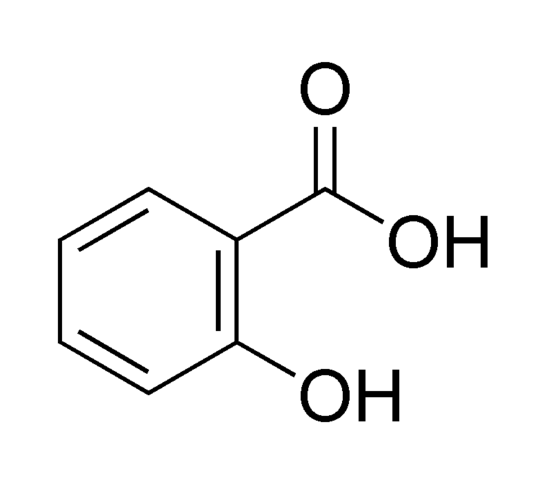 |
| Salicylic acid |
It is used in dermatology - low concentration stimulates the skin epithelium growth
Lactic acid
Is created by lactic fermentation of sugars
In milk, cheese, sauerkraut
Citric acid
In fruits
Part of the Krebs cycle - Intermediate of metabolism of nutrients
| Lactic acid |
Tartaric acid
In fruits
It is used to adjust the acidity of wine, fruit beverages
Ketoacids
Participate in the biochemical processes
Pyruvic acid
It is a product of glycolysis
It is metabolism of alcohol and lactic fermentation
| Pyruvic acid |
Amino acids
COOH - sour
NH2 - alkaline
Colorless, crystalline
Isoelectric point - the pH at which the amino acid is neutral
Dipeptide
Molecule composed of two molecules of the amino acid
If both are the same amino acid = homodipeptid
If the amino acids are different = heteropeptid

No comments:
Post a Comment